Emerald ash borer (EAB), an invasive wood-boring beetle from
Asia, was found in 2 new counties in Indiana in fall
2005, bringing the number of quarantined townships in
the state to 9 after Root and Washington Townships in
Adams County and White River Township in Randolph
County were added. Additional sites were also discovered in LaGrange
and Steuben counties where EAB was found in 2004. It is estimated that
the new EAB populations in Adams and LaGrange counties got their
start 3-5 years ago and are not the result of the beetle's natural
spread. These new infestations are consequences of
artificial movement of the insect, most likely in
firewood, logs for milling, or nursery stock. Emerald
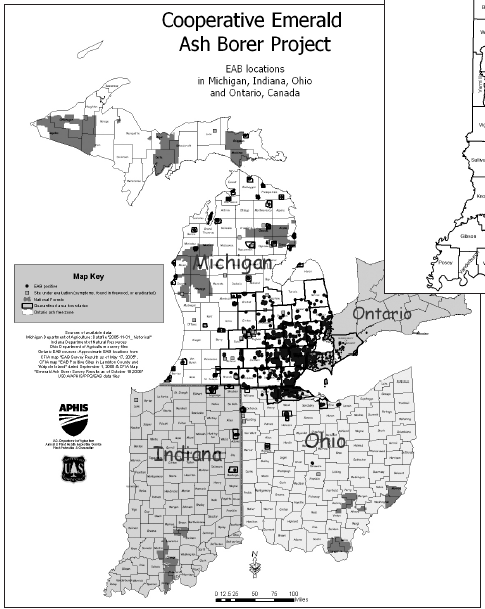
ash borers belong to a group of metallic wood boring beetles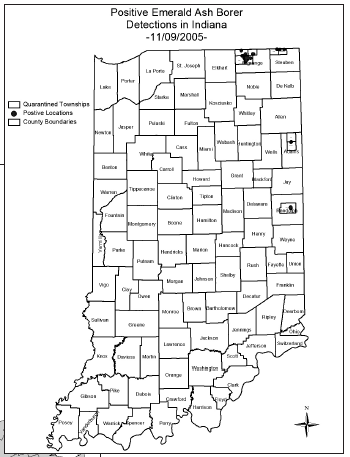 commonly found on woody plants throughout the world. Larvae of
this group are flattened and worm like, and feed beneath bark. First
identified in the Detroit/Windsor area in June 2002,
EAB has been detected throughout Michigan's Lower
Peninsula, in western and northern Ohio, and in
northeast Indiana (see www.emeraldashborer.
info). In its native
commonly found on woody plants throughout the world. Larvae of
this group are flattened and worm like, and feed beneath bark. First
identified in the Detroit/Windsor area in June 2002,
EAB has been detected throughout Michigan's Lower
Peninsula, in western and northern Ohio, and in
northeast Indiana (see www.emeraldashborer.
info). In its native
Asia, EAB attacks and kills ash trees that are
already weakened by disease, environmental
stress, or mechanical damage. However, in North
America, EAB attacks and kills healthy trees as well.
This devastation is possible because, unlike Asian ash
trees, our native trees have no built-in resistance to
EAB. To make
 commonly found on woody plants throughout the world. Larvae of
this group are flattened and worm like, and feed beneath bark. First
identified in the Detroit/Windsor area in June 2002,
EAB has been detected throughout Michigan's Lower
Peninsula, in western and northern Ohio, and in
northeast Indiana (see www.emeraldashborer.
info). In its native
commonly found on woody plants throughout the world. Larvae of
this group are flattened and worm like, and feed beneath bark. First
identified in the Detroit/Windsor area in June 2002,
EAB has been detected throughout Michigan's Lower
Peninsula, in western and northern Ohio, and in
northeast Indiana (see www.emeraldashborer.
info). In its native